For many organisations, Power Apps became the answer to a long-standing challenge: how to build internal business applications without drowning in development cycles. HR teams needed forms, operations needed trackers, finance needed approval flows, and IT needed a way to push out solutions faster. Power Apps democratised much of this by making app building accessible through low-code.
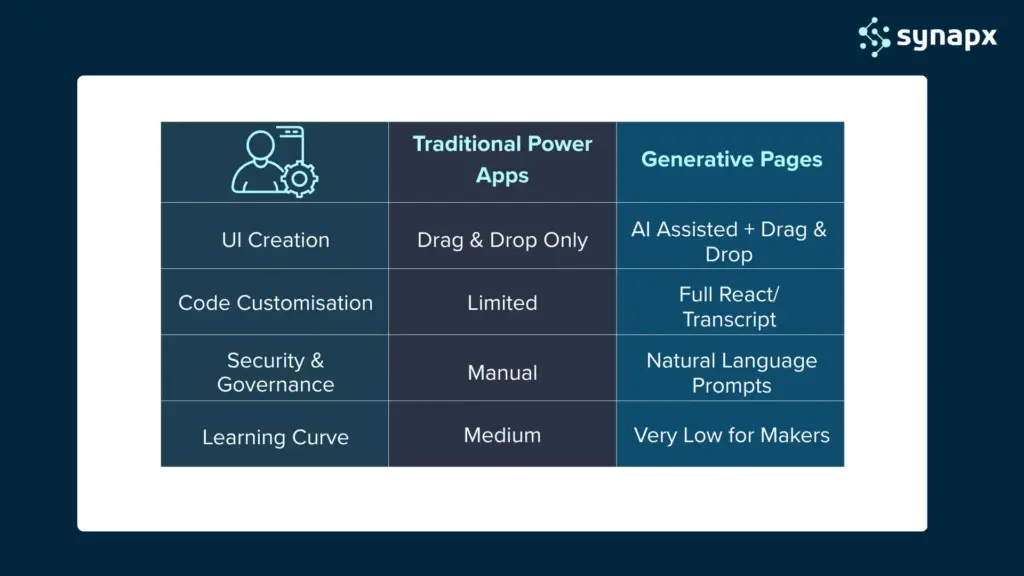
But even with low-code, most apps still require someone to design the interface, structure data, place fields on a screen, format components, and configure logic. It was powerful, but it still required time and expertise.
Generative Pages is one of the most significant evolutions Microsoft has introduced to the platform. Instead of building an app screen manually, you describe what you want, and Microsoft’s AI generates the page for you. No dragging, dropping, or formatting, no guessing where components should go. Just a clear prompt and a fully generated screen.
This guide brings everything together: what Generative Pages are, how they work, where they fit in the Power Apps ecosystem and what they mean for teams that want to build faster without compromising on quality or governance.
What Are Generative Pages?
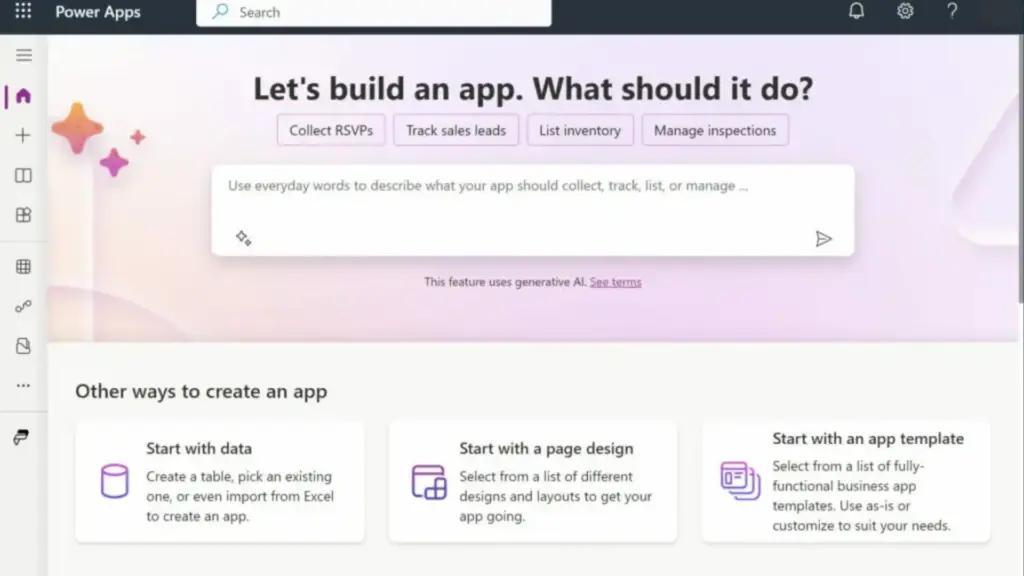
Generative Pages are Power Apps screens created through natural language prompts. If you type: “Create a page to submit service requests with fields for title, priority, description and department.” Power Apps generates a responsive screen with a form, a table to view entries, and the basic logic needed to save and update data. It connects automatically to a Dataverse table, produces a clean, modern layout, and follows the design patterns Microsoft recommends.
You don’t need to align controls, build grids, organise layouts, or write formulas. The AI does the foundation work, so you can focus on refining what matters. For teams who’ve been building apps for years, this feels like skipping straight to the “good part” the moment you start improving the experience instead of constructing it from scratch.
How Generative Pages Actually Work?
Behind the scenes, they rely on structured data. When you select a table and describe the page, Power Apps uses your prompt and the table schema to generate a page built on Microsoft’s modern React component library.
This means:
- Layouts follow consistent patterns
- Data grids load faster
- Editing and display logic is inferred
- Pages adapt naturally to different screen sizes
You can still refine any part of the page manually or ask the AI to adjust specific elements. Think of it as working with a junior developer who produces a solid first draft within minutes.
How They Compare to Canvas and Model-Driven Apps?
Microsoft hasn’t replaced anything. Instead, Generative Pages join Canvas and Model-Driven apps as another option. Canvas Apps are ideal when you want complete control over layout. Model-Driven Apps shine when your application revolves around process, workflow, and structured data. Generative Pages sit between these: fast, consistent, and ideal when you need something functional immediately without deep customisation. Over time, many organisations will use all three, choosing the right tool based on the requirements.
The GPT-5 Advantage: A Significant Upgrade to Generative Pages
The introduction of GPT-5 into Power Apps is one of the biggest improvements to the Generative Pages experience. Earlier AI models were strong at scaffolding ideas, but GPT-5 brings a level of completeness and reliability that feels production-ready.
The differences are immediately noticeable:
- Accelerated Generation: Complex layouts are created in mere seconds, significantly reducing development time and allowing for rapid prototyping of intricate designs.
- Enhanced Code Quality: React components adhere to established best-practice standards, ensuring that the code is not only more maintainable but also easier to understand for future developers.
- Superior Interpretation of Relationships: The system demonstrates an improved understanding of multi-table relationships, enabling it to handle complex data interactions seamlessly and accurately.
- Consistent and Reliable Outputs: With a focus on precision, the outputs generated exhibit a notable decrease in mismatched controls and inconsistencies, leading to a smoother user experience and fewer errors in the final product.
- Advanced Contextual Reasoning: The expanded context window allows for richer logic processing, meaning the system can consider more variables and details, resulting in more nuanced and appropriate outputs.
- Flexibility in Model Selection: The newly introduced model selector empowers users to choose from various AI strengths, allowing for tailored performance based on specific project needs and expertise.
This shift means AI isn’t just filling in blanks; its genuinely helping teams move faster with cleaner, more maintainable outcomes.
Getting Started: Creating Your First Generative Page
To begin, you only need four things:
• Access to a Power Apps environment
• Permission to build model-driven apps
• Dataverse tables set up for your data
• A basic understanding of your data structure
Step 1: Build Your Foundation
Go to make.powerapps.com and open your Dataverse tables.
Choose the table you want to use, for example, Customers, Requests, Projects, or Assets, and select Create an app. Power Apps will generate a model-driven app connected to your table’s views and forms. This becomes the environment where your Generative Page.
Step 2: Add Your Generative Page
Inside the app designer, select Add Page – Describe a Page.
Choose GPT-5 for the best results, confirm your table context, and describe what you want: “Build a customer detail page showing contact info, open cases, a timeline, and a notes section for internal comments.”
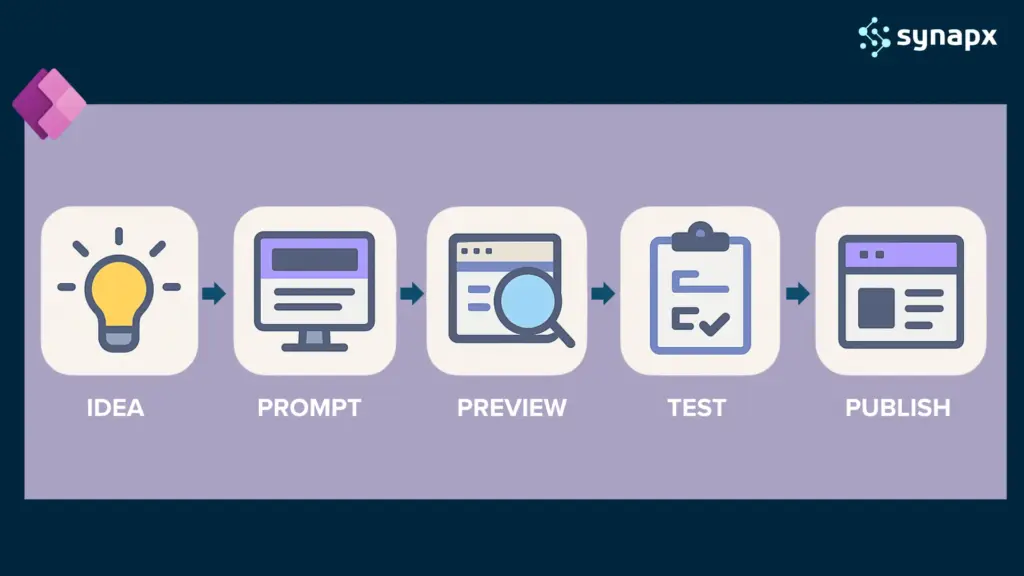
GPT-5 interprets the prompt, understands your data, and produces a complete React page. You now have a functional UI built around your organisation’s data within minutes.
Where Generative Pages Make a Real Difference?
These pages are incredibly useful when you need something quickly but still want a polished result. Teams are already using them to replace manual Excel processes, basic SharePoint forms, and email-based workflows. They’re perfect for internal request systems, simple intake flows, site inspections, compliance acknowledgements, asset logs, and project updates. They also complement Power BI well, especially when users want to write back comments or corrections without leaving a report. For most organisations, the value isn’t just speed. It’s the ability to build small, reliable apps without asking a developer to handcraft a UI from scratch.
Generative Pages are a wonderful starting point, but they’re not built for everything. If your app has multiple steps, complex branching, deep custom interactions or needs to be fully optimised for mobile, you’ll still rely on Canvas or Model-Driven apps. Generative Pages shine when the requirement is straightforward and form-based, not when the experience needs to intricate workflow design.
Why Generative Pages Help Businesses Move Faster?
The true impact of Generative Pages is organisational. Backlogs shrink because teams can create what they need quickly. IT shifts from building everything to curating and governing. Business users become active contributors instead of waiting months for a solution.
Instead of debating layout details or spending hours formatting screens, teams move straight into usage and refinement. This agility is what modern organisations need, especially as expectations for digital tools continue to rise. Even with AI creating much of the experience, good foundations still matter. A well-designed Dataverse table makes the generated page cleaner and more logical. Clear prompts lead to better layouts. Iterating gradually produces stronger results. Governance ensures apps remain secure and manageable over time.
Generative Pages make app development easier, not effortless; they still benefit from thoughtful design, structure and oversight.
AI assistance doesn’t replace governance. Generative Pages inherit Dataverse’s security roles, environment strategies and data policies. Organisations still need to plan where apps live, who can build, how solutions move from development to production, and how usage is monitored.
In other words, Generative Pages change who can build, not the need for governance itself.
How Teams Are Using Generative Pages?
In discussions with teams adopting this capability, a pattern emerges. HR teams build pages to track onboarding tasks. Operations teams create quick audit forms. Finance teams generate approval screens for simple budget requests. Field teams replace Excel inspection logs with clean, AI-generated experiences. The common theme is not complex. It’s momentum. These pages allow teams to modernise everyday processes without waiting for traditional development cycles.
What Generative App Development Means for the Future
Generative Pages are one step in a broader shift. Microsoft is moving toward intent-driven development, where describing what you want becomes enough to generate the foundation of an application. Developers aren’t being replaced; instead, they’re becoming architects, reviewers, and problem-solvers rather than layout designers. As AI matures, we’ll see more components, more automation, and deeper reasoning integrated into the build experience. Generative Pages are simply the beginning.
When organisations start experimenting with Generative Pages, the journey usually begins the same way: someone creates a great prototype in 10 minutes. The excitement spreads. Teams start imagining how many processes they could modernise. And then the first questions arise:
- “How do we secure this?”
- “What happens when we need to scale?”
- “Who decides what goes into production?”
- “Can we trust the data model?”
This turning point is where expertise becomes essential. We’ve supported organisations as their early prototypes evolved into business-critical systems, helping them put the right governance, structure, and design principles in place, not to slow them down, but to ensure they can innovate safely and sustainably.
If your organisation is reaching that moment where early excitement becomes long-term planning, we’re here to help you take the next step with confidence.